


So you need to enable the EPEL repository and then install it like this. Unluckily, pip is not packaged in official software repositories of CentOS/RHEL. To install pip in Linux, run the appropriate command for your distribution as follows: Install PIP On Debian/Ubuntu # apt install python-pip #python 2 Note: We will run all commands as the root user, if you are managing your system as a normal user, then use the sudo command to get root privileges or you can as well configure your system to run sudo command without entering a password, it’s possible. In this article, we will explain how to install PIP on mainstream Linux distributions. Suggested Read: How to Install Latest Python 3.6 Version in Linux
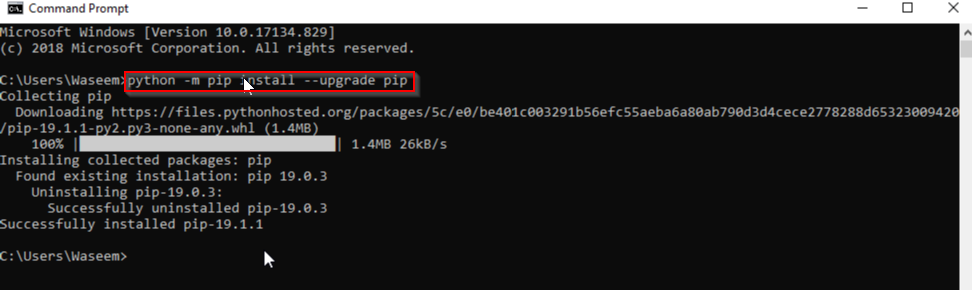
Pip (recursive acronym for “ Pip Installs Packages” or “ Pip Installs Python“) is a cross-platform package manager for installing and managing Python packages (which can be found in the Python Package Index ( PyPI)) that comes with Python 2 >=2.7.9 or Python 3 >=3.4 binaries that are downloaded from.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
